HTTP Cache
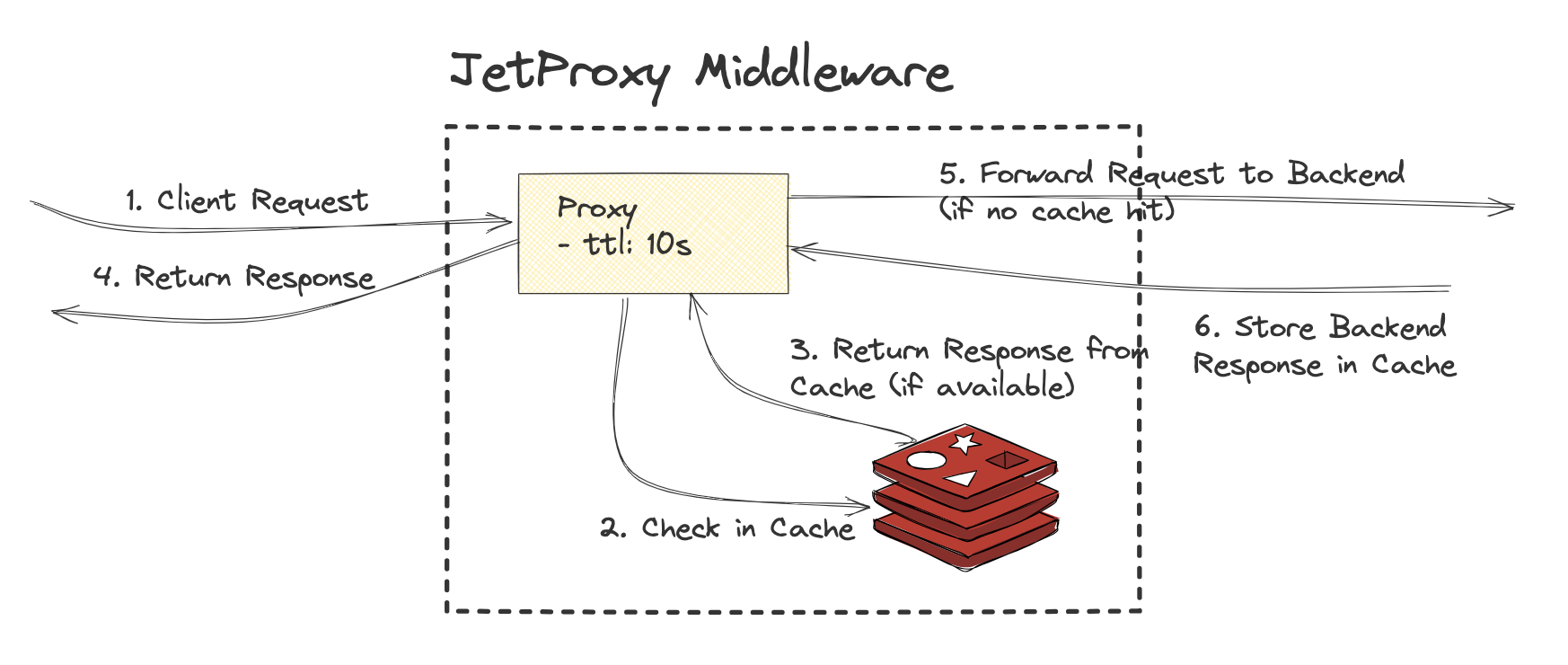
The HTTP cache stores a response associated with a request and reuses it for subsequent requests. Cache types can be enabled based on requirements:
- In-memory Cache: Uses an LRU (Least Recently Used) strategy for efficient memory usage and fast access.
- Redis Cache: Provides distributed caching with a configurable TTL (Time-To-Live) for scalability and persistence.
Setup Storage Cache
storage:
redis:
enabled: true
host: localhost
port: 6379
database: 1
maxTotal: 128 # Maximum total connections in the Redis connection pool
maxIdle: 64 # Maximum idle connections in the Redis connection pool
minIdle: 16 # Minimum idle connections in the Redis connection pool
inMemory: # In-memory cache (stored in application memory)
enabled: true
maxMemory: 50 # Maximum memory allocation for the cache in MB
size: 10000 # Maximum number of entries in the cache
If both redis.enabled and inMemory.enabled are set to true, Redis will be prioritized and used as the primary caching mechanism.
Configuration Examples
proxies:
- path: /httpbin
service: httpbinApi
ttl: 1000
- path: /products
service: productApi
ttl: -1
Additional Notes:
No Cache (ttl: -1)
- Caching is disabled, meaning every request will be forwarded to the backend service without any response being stored or reused.
Supported Methods and Protocol
- Caching only applies to GET requests, as these are typically idempotent and safe for caching.
- The proxy supports caching only for requests over the HTTP protocol. Non-GET methods (e.g., POST, PUT) or requests over non-HTTP protocols will not use caching, regardless of the TTL setting.